



With this filter the user can eliminate closely related proteins from the analysis. This is currently defined as proteins with a sequence identity of 30% or less.
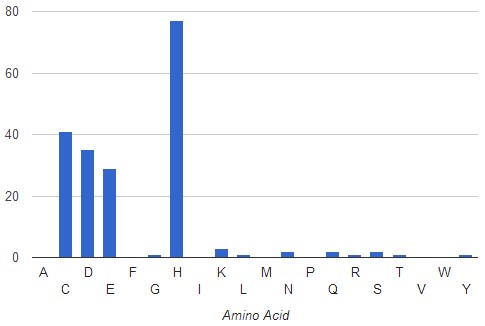
The AFAL analysis without filter, show in the left graph, indicates that most frequent amino acids surrounding the Zn atom at a distance of <3.5A are His, Cys, Asp and Glu with a frequency of occurrence of 77% , 41%, 35% and 29%, respectively. A total of 1833 PDB files was analyzed.
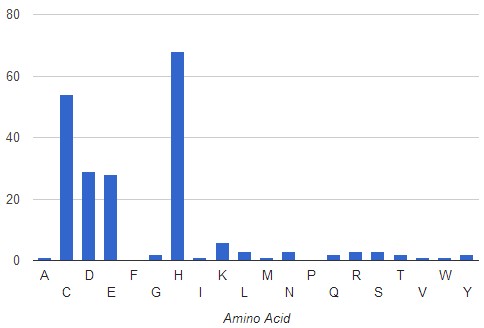
In the case of the redundant filter, analysis of crystalized Zn binding proteins, shows a decrease frequency of occurrence of His residues (68%) and increase for Cys (54%) in comparison to the analysis without filter.
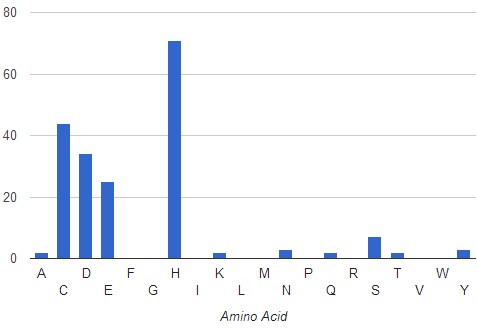
The AFAL profile of all Zn binding proteins crystalized for Escherichia coli (500 PDB files analyzed), indicates that most frequent amino acids surrounding the Zn atom at a distance of <3.5A are His, Cys, Asp and Glu with a frequency of occurrence of 71% , 44%, 34% and 25%, respectively.
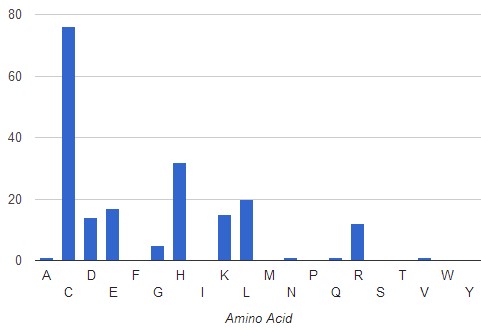
In the case of the hyperthermophile Thermus thermophilus, analysis of crystalized Zn binding proteins (219 PDB files analyzed), shows a higher frequency of occurrence of Cys residues (76%) at a distance of <3.5A from the Zn atom. The mayor presence of Cys can be explain because the formation of this disulfide bond increases the thermal stability of the protein (Hirano, et al., 1998. Biochemistry, 37(36), 12640–8)